
When manufacturing operations still rely on traditional methods, companies face challenges such as labor shortages, increasing production complexity, tight delivery schedules, and cost control. Decisions often depend on experience and manual judgment, making it difficult to act effectively amid massive amounts of information. Data from various systems—such as machine parameters, yield records, production progress, and quality issues—are often scattered and cannot be integrated in real time, limiting both efficiency and accuracy.
As AI technology continues to mature—especially with breakthroughs in language understanding, data integration, and logical reasoning—these challenges are gradually being overcome. AI is no longer just a topic for research labs; it is now entering the shop floor, becoming a practical tool to enhance management efficiency and smart production.
We are witnessing how AI is turning complex data into clear decision-making power, helping companies navigate through information overload to identify the best course of action. DigiHua Intelligent Systems is embracing this wave of transformation by offering solutions tailored to industrial needs—empowering factories to evolve from data collection to insight-driven operations as truly smart factories.
In this article, we’ll break down what “digital transformation in manufacturing” truly means. It’s more than just implementing systems—it’s about using data to drive smarter decisions. We’ll explore the core of this transformation, especially how it’s being reshaped in the age of AI. Most importantly, we’ll discuss practical ways a smart manufacturing system provider like DigiHua Intelligent Systems can help you reduce costs, improve efficiency, and leverage AI tools to boost performance.
Let’s dive in.
I.AI is here to automate repetitive work—not to replace your worth
What Are Common Repetitive Tasks in Manufacturing Plants?
On the shop floor, a large number of repetitive tasks need to be handled every day. These include checking machine statuses, compiling downtime records, filling out yield reports, preparing monthly summaries, and tracking order progress or raw material inventory across departments. Such processes often consume significant time and manpower, yet require minimal judgment or creativity. These are known as high-frequency, low-variance tasks—among the most common in factories and the most suitable for AI-driven automation.
That still might sound a bit abstract, so here’s an example:
When a manager asks, “Which machine had the longest downtime yesterday? How long did it stop? And why?”, the traditional process would involve an engineer logging into the system, exporting a CSV file, importing it into Excel, organizing the data, and finally pasting a chart or summary into the report. This back-and-forth could easily take 30 minutes—and there’s no guarantee the logic is consistent or the visuals are clear every time.
Now, with AI tools, you can simply type the question in natural language and instantly get a visualized answer. No SQL writing required. Engineers save time, sales teams can access data directly, and managers get a clear view of what’s happening. Data communication is no longer held back by technical barriers.
What AI truly replaces are the repetitive tasks that don’t require human judgment—not the value people bring. On the contrary, it frees up human resources: engineers can focus more on root cause analysis, process optimization, and cross-functional collaboration; sales teams can generate faster customer forecasts and strategic proposals; and managers can concentrate on operational decisions and performance management.
Simply put, AI handles repetitive work—so you can focus on what truly matters.
Human value lies in judgment, creativity, communication, and collaboration.
AI is the tool that amplifies these strengths.
II.AI Meets Manufacturing
Before the AI wave swept through manufacturing, DigiHua Intelligent Systems had already been laying the groundwork for digital transformation. From data consolidation and system integration to the digitalization of process knowledge, we help manufacturers turn fragmented machine signals, work order flows, and quality records into a unified, visualized operations platform. This creates a production environment that is measurable and predictable—laying the essential foundation where AI can truly deliver value.
As we enter the era of AI, attention has shifted toward more advanced applications—such as equipment failure prediction, intelligent scheduling, smart quoting, and automated task dispatching. By analyzing historical data, AI can uncover patterns, predict maintenance needs, recommend machining routes, estimate quotes, and even trigger downstream processes. These applications can significantly boost efficiency and reduce errors across operations.
But amid all the excitement about what AI can do, a few critical questions are often overlooked:
– Is your organizational knowledge already structured, and is your data clean enough?
– Who is responsible for validating AI-generated recommendations?
– Does the language model truly understand the technology—or the industry context it operates in?
These issues aren’t just technical challenges—they determine whether AI can truly be implemented on the ground. DigiHua Intelligent Systems positions itself in these often-overlooked blind spots, acting as the bridge between AI and real-world manufacturing operations.
We don’t just deliver technology; we design AI assistant systems grounded in the manufacturing context—built to understand industrial vocabulary and align with shop-floor workflows. From where the data comes from, who uses it, to how it improves over time, our approach is rooted in real-world practice. DigiHua delivers AI solutions truly built for industrial professionals.
III.Is AI truly incapable of replacing human decision-making?
As AI continues to learn and evolve rapidly, it’s not uncommon to hear experts raise the question:
Will there come a day when AI can replace humans in making decisions?
It’s clear that AI has demonstrated unprecedented speed and accuracy in data processing and predictive analysis. In manufacturing especially, AI is rapidly transforming the way we interpret reports and make decisions.
Turning “Data” into “Real-Time Situational Awareness”
AI can instantly consolidate data from MES, ERP systems, and sensors—transforming it into dashboards, trend charts, and anomaly alerts. This allows frontline managers to grasp the situation at a glance and saves significant time previously spent on manual data processing.
From Static Reports to Predictive Systems
By leveraging historical data and logical models, AI can proactively forecast production bottlenecks, delay risks, and capacity anomalies. It can also auto-generate daily, weekly, and monthly reports—supporting cross-departmental collaboration and faster decision-making.
Beyond Analysis: Proactive Optimization Recommendations
AI can cross-analyze scrap reasons, yield variations, and equipment utilization, and compare them with patterns from other factories or historical data. It automatically identifies root causes, suggests improvement actions, and can even trigger task assignments or reschedule production plans.
Making Tacit Knowledge Explicit: Supporting SOPs and Quotation Estimates
AI can learn on-site process logic and expert experience, automatically generating cost estimates, drafting SOPs, suggesting production schedules, and recommending workforce allocation. This enables companies to make better use of internal know-how and turn expertise into actionable systems.
AI may drive decisions—but can AI ever fully replace human judgment?
We know that AI excels at data analysis, pattern recognition, and logical computation.
But in real-world decision-making, there are still several irreplaceable human strengths—such as contextual understanding and situational judgment, the ability to adapt on the fly, intuition based on experience, ethical reasoning and accountability, and building trust and consensus within a team.
Therefore, we can say that AI can help us interpret data faster and make decisions with greater accuracy—but it cannot replace human judgment when it comes to context, values, and responsibility.
In a data-driven factory, humans are not being replaced—they are evolving.
From data processors to strategy designers, from process operators to problem solvers.
That is the true value of industrial AI.
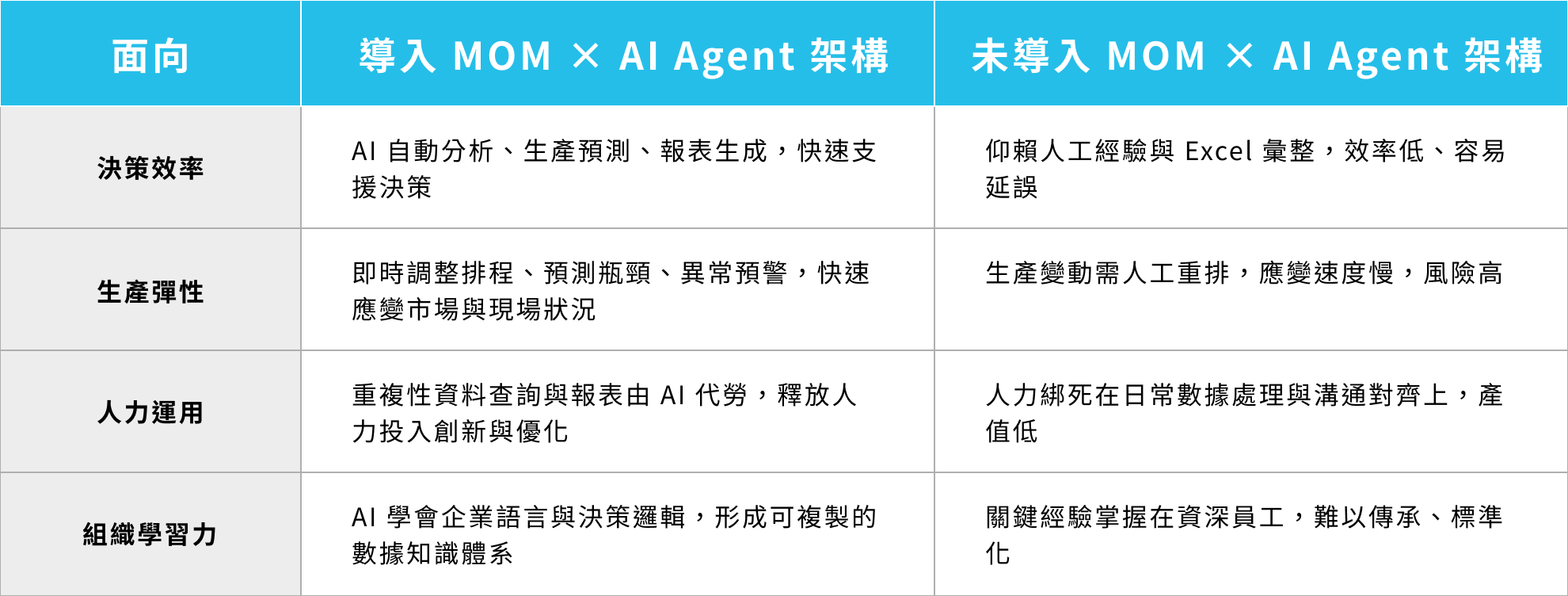
IV. DigiHua’s Integration of MOM Architecture and AI Agents to Enable Smarter Manufacturing
The first step in manufacturing digital transformation is gaining full visibility and control over factory operations.
DigiHua has long been dedicated to this journey by building a robust architecture centered on MOM (Manufacturing Operations Management).
This framework integrates five key modules—scheduling, production, quality, equipment, and decision support—enabling manufacturers to establish a data-driven operational foundation. It supports core functions such as shop floor management (MES), capacity scheduling (APS), process quality control (QMS), and real-time operational visibility (FWR).
The core value of the MOM architecture lies in enabling companies to gain real-time visibility into their operations, while laying the foundation of data standards and management processes essential for smart manufacturing and AI-driven decision-making.
To boost efficiency, we’ve integrated the MOM architecture with AI Agents—transforming operational data into decision-making power.
DigiHua implements AI Agents with industry-specific semantic understanding. These agents preserve existing systems and user habits, while seamlessly combining semantic search, image recognition, and reasoning logic. In doing so, AI becomes more than an add-on analytics tool—it becomes a true digital member of the factory team.
What we do to turn smart manufacturing into reality—powered by our core technologies.
Semantic Query Engine
Employees can ask questions in natural language—such as “Which production line had the highest scrap rate this week?”—and AI instantly responds with charts and trend insights.
Image Recognition and Process Path Recommendations
AI can interpret lightweight 3D models and, by referencing the process knowledge base, automatically suggest machining sequences and scheduling recommendations.
Anomaly Reasoning and Automated Task Dispatching
AI identifies production anomalies and proactively triggers processes such as maintenance, rework, or quality improvement.
By integrating these AI technologies, DigiHua not only helps our clients better understand their data, but also transforms decision-making from experience-based guesswork into a process of dynamic collaboration grounded in logic and data.
But implementing a system isn’t a one-time test—it’s a long-term practice in observation.
We’ve found that those who can ask the right questions are the ones who can truly harness the power of AI and unlock its value.
In factory operations, how teams observe issues, frame questions, collaborate, and make decisions determines whether they can identify bottlenecks and continuously improve through everyday operations.
For manufacturers, observation and judgment are the most critical—and least replicable—forms of long-tail value in digital transformation.
DigiHua’s approach is not to replace that value with AI, but to help companies amplify it.
V. Typical Questions and Concerns When Adopting AI
Is the integration of MOM architecture and AI Agents always smooth?
Fortunately, with nearly 30 years of implementation experience, DigiHua helps enterprises navigate the journey step by step—ensuring a smooth and confident transformation.
Here are some of the common challenges we encounter during real-world deployments, along with how we address them:
Overwhelmed by Data? Not Sure Where to Start? (Do you still need to look?)
✅ DigiHua helps you integrate heterogeneous data sources such as MES, APS, and QMS. With semantic search in place, a single question is all it takes to retrieve the data and trends you need—no more manual Excel comparisons.
Struggling to Transfer Expert Knowledge? Slow Onboarding for New Staff? (Do You Still Need to Train Everything Manually?)
✅ By combining knowledge graphs with expert-based modeling, AI learns industry-specific terminology and practical logic. It then transforms this into structured recommendations—helping new team members understand and act quickly, without relying solely on manual training.
Long Reports Slowing Down Decisions? Decisions Getting Delayed? (Still Spending Hours on It?)
✅ With AI-powered auto-summary and chart generation, complex data becomes instantly understandable—in under 3 minutes. Managers can quickly grasp the full picture and stay focused on what matters most.
DigiHua believes that implementation is not a one-way delivery of tools—it’s a shared journey of growth with our clients.
We bring the architecture and technology; our clients bring the context and real-world environment.
Through ongoing collaboration, we co-create a digital rhythm that truly fits each factory’s unique operations.
VI.Conclusion:More Than AI—A Smarter Way to Work, Together
AI makes tools and outputs more accessible than ever—but real industry experience remains rare and invaluable.
AI can help us retrieve information faster, analyze trends, automate scheduling, and even generate maintenance suggestions and pricing forecasts.
Its capabilities have undeniably made factories more efficient—but they also raise new questions:
Who defines the right problems to solve?
Who can assess the risks and opportunities behind the data?
And who can combine experience with systems to make the right decisions?
AI is a powerful assistant—but it won’t think about value for you.
The real difference lies in this:
Can we stay focused during this transformation on strengthening our observation, judgment, and cross-functional collaboration—
and become leaders who not only understand the production line and the data, but also make better decisions because of it?
In the age of AI, those who can leverage its power—while combining it with deep industry expertise and strong decision-making—will have the greatest competitive advantage.
📣 Share this article with a friend in manufacturing—they might just find a smarter way to collaborate with AI.



