Discrete manufacturing metal and hardware
industry solution

Challenges in Industry Management
- Forecasting for rough (casting/forged) products are often done manually and based on experience, resulting in either overstocking, increasing inventory cost, or underestimating, leading to delayed delivery times.
- In order to plan and schedule orders, it is necessary to consider not only the available rough products but also to have real-time access to materials, work-in-progress, and production capacity to determine if delivery times can be met.
- The manufacturing process is complicated, and despite allowing for buffer times, actual production time is low due to stoppages and downtime, making it difficult to shorten the production cycle.
- It is difficult to control the assembly and packaging process as the production progress cannot always follow a predetermined plan, and ensuring that all parts are available for packaging is challenging.

Collaboration between upstream and downstream partners is common in the casting industry, with the main processes being the in-house precision casting and outsourced CNC machining, heat treatment, and surface treatment. However, the lack of digitization and reliance on manual operations makes it difficult to monitor cross-chain support, production schedules (such as processes, quantities, and delivery dates), quality information, and other aspects. As a result, the supply chain delivery accuracy is only around 70% (far lower than the automotive industry’s delivery accuracy of 100%).
The information obtained in the 3K traditional industry is still based on outdated indicators and lacks complete traceability. The process of intelligentization in this industry is slow, and manual paper-based operations are still common. This belongs to the “back-end” of smart manufacturing, where the information is not timely, not accurate, and lacks completeness, making it difficult to respond quickly to the endless changes in the manufacturing process. It is also difficult to meet the flexible production needs of small batches and multiple varieties.
Quality and yield have always been a concern in manufacturing. For casting products, quality inspection can only be conducted at the final process station or after a certain manufacturing process. However, manual inspection standards are difficult to unify, resulting in an average inspection rate of only 75%. This makes quality control difficult and accuracy and yield difficult to improve, thus making it difficult to enter high-quality markets.
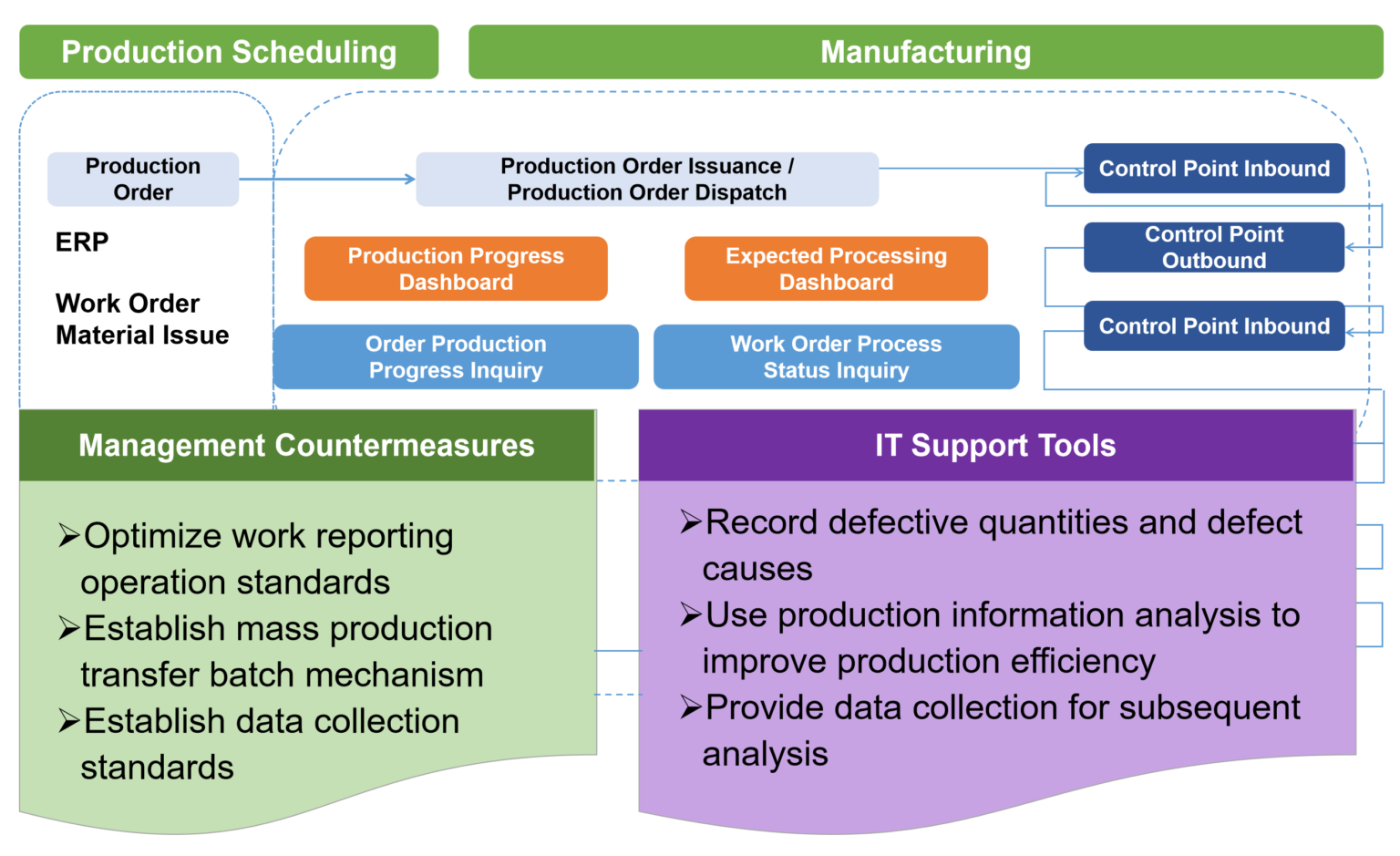
Industry Solutions
Knowledge
Demand management, capacity assessment, lead time.
Mechanisms
Production pacing mechanism Material tracking and expediting mechanism Scheduling and dispatching mechanism Production progress tracking mechanism Equipment management mechanism
Processes
Demand forecasting and clearance process Standard working hours definition process Production dispatching process Production progress reporting process Production progress tracking and expediting process Equipment status change process Equipment integration abnormal handling process.
Tools
MDS offset maintenance operation Materials follow-up and expediting table sMES basic setup planning Product standard labor and production resource cycle time sMES dispatching sMES progress reporting planning sMES machine status and utilization planning.
Indicators in production management
Work order completeness rate Work order on-time start rate Expected order delivery date Production delivery lead time Dispatch completion rate
Monitoring
Purchase order overdue alert, order/work order shortage alert, order delay days, internal bottleneck load alert, dispatch plan achievement report.
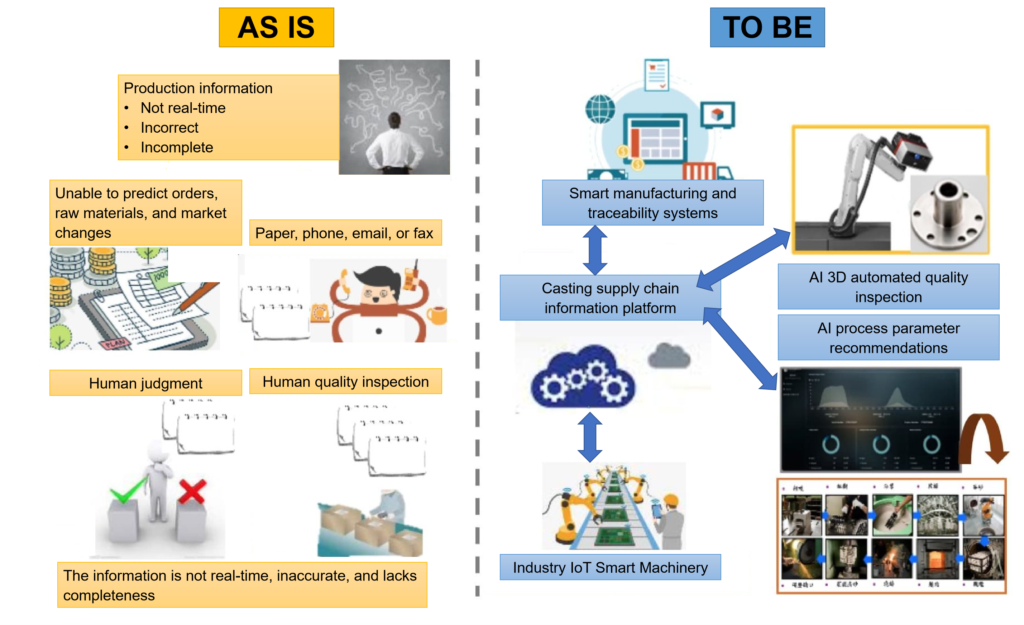
Industry Solutions
Return on Investment (ROI)
By implementing the solution, the accuracy of material planning can be improved, resulting in a 15% reduction in material inventory. In addition, the efficiency of the manufacturing process can be improved, resulting in labor cost savings due to an expected 18% increase in yield and a reduction in manual welding, rework, and polishing.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Can reduce secondary rates and reduce the defect occurrence rate by 10%. The utilization rate is increased to 90%, the production efficiency is maintained at 85%, and the yield rate is increased to 80%, resulting in a 9% increase in OEE.
Shortening Lead Time
The collection of cross-factory production progress and quality information will be improved from manual operation to digital streaming. It is expected that the lead time can be shortened by 20%.


